HTML::FormHandler & jQuery Validator
OVERVIEW
HTML::FormHandler
HTML::FormHandler maintains a clean separation between form construction and form rendering. It allows you to define your forms and fields in a number of flexible ways. Although it provides renderers for HTML, you can define custom renderers for any kind of presentation. HTML::FormHandler allows you to define form fields and validators. It can be used for both database and non-database forms, and will automatically update or create rows in a database. It can be used to process structured data that doesn't come from an HTML form.
HTML::FormHandlerX::Form::JQueryValidator
The HTML::FormHandlerX::Form::JQueryValidator is a simple role which provides convinient mechanism to create a simple jQuery validation profile from our form definition.
jQuery Validator
jQuery Validator makes clientside form validation easy and at the same time provides a lot of options to customize the validation plugin to your specific needs. The plugin comes with useful commonly used set of validation methods such as validation URL, email addresses, zip codes, phone numbers, credit card numbers and etc. All these methods come with default error messages which are available in more than 30 different languages.
Simple Order Form
Let's wrap all together and create a simple order form. First of all we start with our form defition. Our form looks pretty standard including First & Last name, Address, City, Zip Code, Country and Credit card information.
package MyApp::Form::Order;
use MooseX::Types::CreditCard qw/CardNumber CardSecurityCode CardExpiration/;
use HTML::FormHandler::Types ':all';
use HTML::FormHandler::Moose;
extends 'MyApp::Form::Base';
with 'HTML::FormHandler::Widget::Theme::Bootstrap';
has '+item_class' => ( default => 'Order' );
has_field 'first_name' => (
type => 'Text',
required => 1,
required_message => 'Please enter your first name.',
label => 'First name',
);
has_field 'last_name' => (
label => 'Last name',
type => 'Text',
required => 1,
required_message => 'Please enter your last name.',
);
has_field 'address' => (
label => 'Address',
type => 'Text',
required => 1,
required_message => 'Please enter your last name.',
);
has_field 'zip_code' => (
label => 'Zip code',
type => 'Text',
apply => [ Zip ],
required => 1,
required_message => 'Please enter valid zip code',
);
has_field 'city' => (
label => 'City',
type => 'Text',
required => 1,
required_message => 'Please enter city.',
);
has_field 'country' => (
label => 'Country',
type => 'Select',
empty_select => 'Choose country',
required => 1,
required_message => 'Please enter your country.',
);
has_field 'card_type' => (
label => 'Credit card type',
type => 'Select',
);
has_field 'card_number' => (
label => 'Credit card number',
type => 'Text',
element_class => [qw/creditcard/],
apply => [ CardNumber ],
required => 1,
required_message => 'Please enter valid credit card number.',
);
has_field 'exp_date' => (
label => 'Expiration',
type => 'Date',
format => '%d/%y', # example: 12/12
element_class => [qw/input-mini date/],
element_attr => { placeholder => 'Ex. 12/12', },
required => 1,
required_message => 'Please enter valid expiration date',
);
has_field 'cvc_code' => (
label => 'Card Verification Code',
type => 'Integer',
element_class => [qw/input-mini number/],
apply => [ CardSecurityCode ],
required => 1,
required_message => 'Please enter CVC',
);
has_field 'comment' => ( type => 'Text' );
has_field 'submit' => ( type => 'Submit', value => 'Process order', element_class => ['btn'] );
sub options_card_type {
my $self = shift;
my @options = map { $_ => $_ } qw(Visa MasterCard AmericanExpress Discover);
return \@options;
}
sub options_country {
my $self = shift;
my @options = (
{ value => 'US', label => 'United States' },
{ value => 'DE', label => 'Germany' },
{ value => 'FR', label => 'France' },
{ value => 'BG', label => 'Bulgaria' },
);
return \@options;
}
__PACKAGE__->meta->make_immutable;
no HTML::FormHandler::Moose;
1;
Let's take a look at our form fields keywords. Keywods like type, label, required, required_message are mostly self-explanory. The apply keyword specify an array refference of constraints and coercion which are executed at validation time. The element_class defines an array of classes to include on the defined element. This is pretty convinient, because jQuery Validator allows us to specify the validation methods as classes. For our convinience we've created a small base class called MyApp::Form::Base.
package MyApp::Form::Base;
use utf8;
use HTML::FormHandler::Moose;
extends 'HTML::FormHandler';
with 'HTML::FormHandlerX::Form::JQueryValidator';
has_field validation_json => ( type => 'Hidden', element_attr => { disabled => 'disabled' } );
sub default_validation_json { shift->as_escaped_json }
sub html_attributes {
my ( $self, $field, $type, $attr ) = @_;
if ($type eq 'label' && $field->{required}) {
my $label = $field->{label};
$field->{label} = "$label *" unless $label =~ /\*$/; # we append it once only
}
return $attr;
}
1;
Our Base form class have 2 purposes. First, we define a html_attributes
method, which appends a '*' to the label of each required field. Second, it
adds a hidden field containing the jQuery Validation profile as encoded json.
We don't want the validation_json to be submitted when we submit our form
data and that's why we add an element attribute disable to the
validation_json field.
Now let's display our form and enable the jQuery Validation Plugin.
# In our Controller
...
use MyApp::Form::Order;
has 'order_form' => ( isa => 'MyApp::Form::Order', is => 'rw',
lazy => 1, default => sub { MyApp::Form::Order->new } );
BEGIN { extends 'Catalyst::Controller' }
sub order : Chained('base') PathPart('order') Args(0) {
my ( $self, $c ) = @_;
my $result = $self->order_form->run(
params => $c->req->parameters,
action => $c->uri_for($c->action, $c->req->captures ),
);
$c->stash( form => $result );
return unless $result->validated;
$c->res->redirect( $c->uri_for('/') );
}
1;
Our template file contains just few lines. The HTML::FormHandler provides a render method, which renders the entire form for us!
[% form.render %]
$(document).ready(function() {
if ($('#validation_json').length > 0) {
var validationJSON = JSON.parse(decodeURIComponent($('#validation_json').val()));
$('.form-horizontal').validate({
rules: validationJSON.rules,
messages: validationJSON.messages
});
}
});
And that is all! We have nice looking form, both validated front-end and server-side and automatically integrated with DBIx::Class using the HTML::FormHandler::TraitFor::Model::DBIC trait.
And here is the final example:
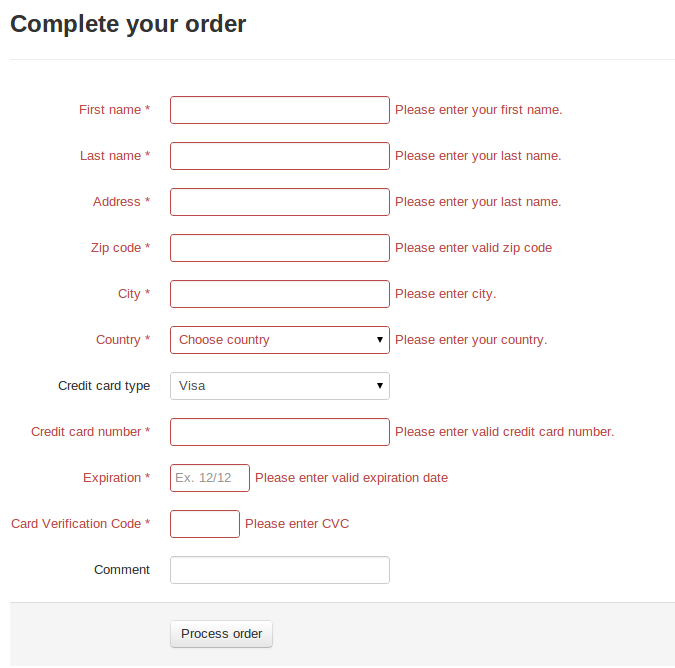
Demo
Please check the live demonstration: http://formhandler-perl.dotcloud.com/examples/order/
For More Information
For more information please check: HTML::FormHandler::Manual::Tutorial, HTML::FormHandlerX::Form::JQueryValidator, jQuery Validator Plugin
Summary
Author
Dimitar Petrov <dcpetrov@cpan.org> dpetrov
- Previous
- Next